Shared and Embedded Parameters
Shared and Embedded parameters are not specific types of parameters, instead they refer to two different ways in which parameters might be used.
Shared Parameters
There is no limit on the number of times a user parameter can be used or linked to an FME parameter. The value obtained from a user parameter can be used as many times as is required.
When a parameter is used in two or more places it can be described as a shared parameter.
For example, a workspace has a user parameter called TOLERANCE (here being used inside a Generalizer):
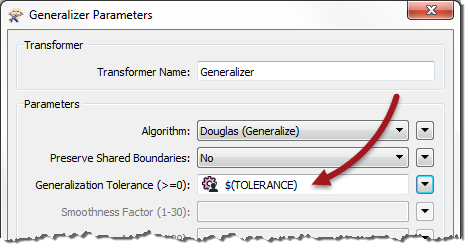
However, the workspace author has decides to apply the same parameter in three places in total; two Generalizers and a Snapper:
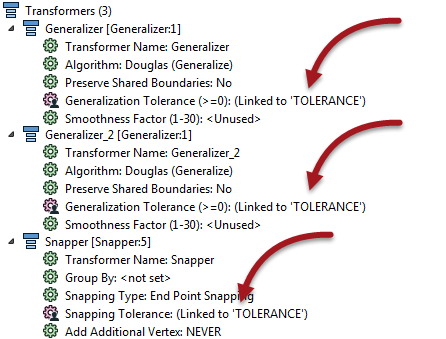
The advantage is that the same value can be used without the user having to enter it multiple times.
Embedded Parameters
Sometimes in FME, string values need to be constructed from multiple components. When a string is constructed in such a way as to use multiple user parameters, we call it Embedding Parameters.
For example, here a file being written is constructed from two user parameters: one is a fixed output path and the other is a user's name:
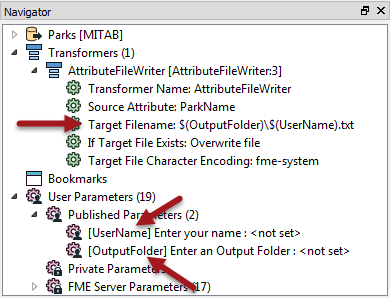
Basically a user parameter is created to accept the user's name (UserName) and a second parameter (OutputFolder) accepts a folder to write output. The FME parameter on an AttributeFileWriter transformer constructs a single value from these two user parameters.
Similarly, the value from one user parameter can be embedded inside the definition of another! You might call this scenario nested user parameters.
| Ms. Analyst says... |
| Going forward, another example of embedded/nested user parameters can be found in the section on Private Parameters |