| Exercise 3 | Dynamic Community Mapping Data Translations |
| Data | Community Mapping (Esri File Geodatabase) Addresses (Esri File Geodatabase) |
| Overall Goal | Create a dynamic workspace to translate any Geodatabase dataset to a format of the end-user's choice |
| Demonstrates | Dynamic Formats |
| Start Workspace | None |
| End Workspace | C:\FMEData2016\Workspaces\DesktopAdvanced\ReadWrite-Ex3-Complete.fmw |
In the previous exercise, a workspace was generated to translate a Geodatabase dataset into a number of formats using the Generic Writer.
However, that workspace had a limitation with the output attributes (every output dataset got all of the source table attributes) and you also feel it would be useful if that workspace could handle any source Geodatabase, not just the community maps dataset.
So, let’s create a new workspace to handle that scenario.
1) Start Workbench
Start FME Workbench and begin by generating a workspace as follows:
| Reader Format | Esri Geodatabase (File Geodb API) |
| Reader Dataset | C:\FMEData2016\Data\CommunityMapping\CommunityMap.gdb |
| Writer Format | Generic (Any Format) |
| Writer Dataset | C:\FMEData2016\Output\Training |
| Workflow Options | Dynamic Schema |
2) Inspect Workspace
Inspect the newly created workspace:
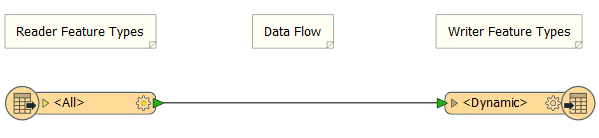
There is one Reader feature type and one Writer feature type. The Reader feature type shows a list of attributes, but the Writer feature type doesn’t. It is, however, labelled Dynamic.
Again, there will be a user parameter for the Feature Types to Read and the output format.
If you wish, create a more-limited version of the output format parameter, by following steps 3-5 in the previous exercise; although this isn’t totally necessary for what we’re doing here.
But don’t delete the Source Dataset user parameter; we’ll need that shortly.
3) Run Workspace
Run the workspace with the prompt option set.
When prompted, select some source tables and set the output format. The workspace will run to completion. Check the output to ensure it is all correct.
4) Re-Run Workspace
Now run the workspace again.
This time click the browse button for the source Geodatabase and browse to C:\FMEData2016\Data\Addresses\Addresses.gdb
Choose the feature types to read and this time you will be presented with a list of feature types from the newly selected Geodatabase.
Click OK to run the workspace again. Inspect the output. Notice that the output feature types are all as listed in the original data. Also notice that the attributes are as in the original too!
From this we can see that a dynamic workspace is capable of handling any source schema and writing it out to a new dataset just as it was in the source data.
| CONGRATULATIONS |
By completing this exercise you have learned how to:
|