| Exercise 1 | Taxation Report Project |
| Data | Building Footprints (AutoCAD DWG) Zoning Data (MapInfo TAB) |
| Overall Goal | Create a taxation report for each building |
| Demonstrates | Constructing attribute values |
| Start Workspace | C:\FMEData2016\Workspaces\DesktopAdvanced\Attributes-Ex1-Begin.fmw |
| End Workspace | C:\FMEData2016\Workspaces\DesktopAdvanced\Attributes-Ex1-Complete.fmw |
The annual property tax reports are due to be calculated and it is decided to use FME to carry out the processing. You must set up a workspace that calculates tax values for each building (based on size and zoning) and create a plain text file containing the results.
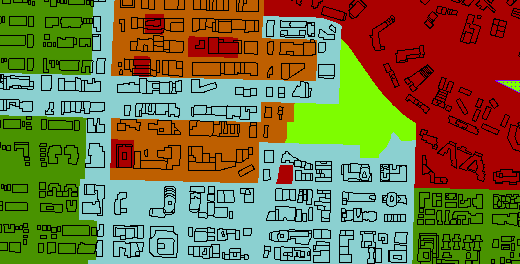
1) Inspect Source Data
Inspect the two source datasets you will be working with. They are:
| Reader Format | MapInfo TAB (MITAB) |
| Reader Dataset | C:\FMEData2016\Data\Zoning\Zones.tab |
| Reader Format | Autodesk AutoCAD DWG/DXF |
| Reader Dataset | C:\FMEData2016\Data\Parcels\BuildingFootprints.dwg |
| Reader Parameters | Group Entities By: Attribute Schema |
2) Open Workspace
Open the workspace C:\FMEData2016\Workspaces\DesktopAdvanced\Attributes-Ex1-Begin.fmw. This is what you have created so far in order to set up Readers and Writers and a couple of preparatory transformations:
Open the parameters dialog for each transformer in turn.
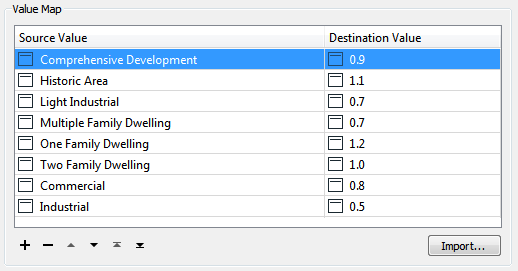
The AttributeValueMapper is mapping from zone category to a TaxMultiplier value:
The GOIDGenerator is merely creating a unique ID for each building footprint.
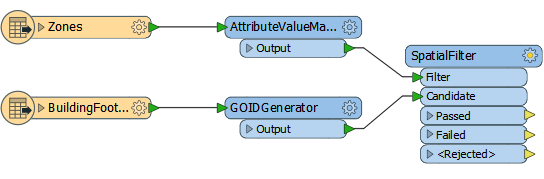
3) Add SpatialFilter
The first thing to do is transfer zoning information onto the building footprints. Add a SpatialFilter transformer to the workspace, with the zones as the Filter features and the buildings as the Candidates:
Open the parameters dialog. Under Tests to Perform, select Intersects and Contains.
The other parameters can remain as their default; but just check that Filter Type = Multiple Filters and that Pass Criteria = Pass Against One Filter
You may want to add an Inspector and run the workspace to ensure that the building features do - as expected - emerge from the SpatialFilter:Passed output port.
4) Add AttributeManager
Add an AttributeManager connected to the SpatialFilter:Passed output port and open the parameters dialog.
The first task is to create a numeric value for the taxation amount. So add a new attribute called TaxAmount and click the drop-down arrow to the right and choose the option for Open Arithmetic Editor:

5) Calculate Tax Amount
The calculation for the tax amount is:
Building Footprint x Tax Multiplier x Tax Rate
...where Building Footprint is the area in square metres, Tax Multiplier is the value relating to the Zone Type, and Tax Rate is a value that changes each year and so should be provided by the user.
The result should also be rounded off to two decimal places.
So... start out by locating Area under FME Feature Functions and double-clicking it to add the area of the building footprint to the equation:

Next add a multiplication symbol, and locate the TaxMultiplier attribute and double-click it to add it to the equation:
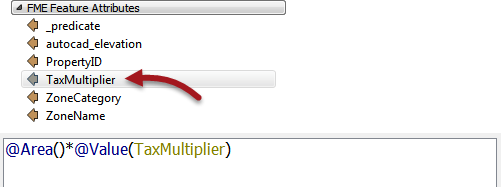
Add another multiplication symbol. Now we need a user parameter to accept input from the user. We haven't defined it yet, but we can still do that inside the editor dialog.
Locate the published parameters section and click on <Create Published Parameter>
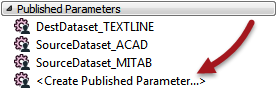
When prompted create a new parameter called TaxRate of type Float. Enter a default value of 0.2 and ensure the Optional checkbox is not checked:

Click OK and the parameter is added to the calculation:

Now we just need to round the result to two decimal places. Unfortunately the round function in this editor rounds only to an integer, so we must multiply the result by 100 first, then divide by 100 after.
So, add a multiplication symbol and the fixed value 100:
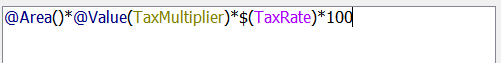
Now enclose all of the current statement inside a round function:

Finally add a division symbol and divide the whole statement by 100:
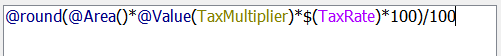
Click OK to close this dialog but keep the AttributeManager parameters open.
6) Create Tax Report String
The final task is to create a string of text that we can write to a report file. In this case the end-users of the information wish to receive a plain text file in the following structure:
Property: <PropertyID> Tax Value: <TaxValue> Dated: <Current Date>
So, inside the AttributeManager create a new attribute called text_line_data - this will match the output schema. Then click the drop-down arrow and open the text editor dialog.
Enter fixed values and add the attributes in the appropriate places to get the correct output:

Then use the Timestamp function with the format ^d-^m-^Y to create a date in the correct format:

To get carriage returns in the output we need to specifically add those characters to the editor. To see such characters, select Options > Show Spaces/Tabs
Then locate Carriage Return (\r) in the Special Characters menu and add one for each line:
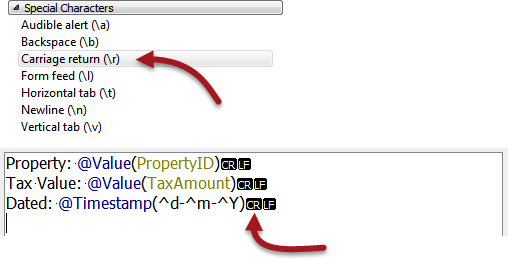
Now click OK to close the dialog and OK again to close the AttributeManager dialog.
7) Connect Schema, Run Workspace
Connect the AttributeManager:Output port to the Text File Writer feature type:
Save and then run the workspace. The result should be a text file that looks like this:

| CONGRATULATIONS |
By completing this exercise you have learned how to:
|