Existing Boundaries
An existing area feature can be read into a workspace, but it cannot then be forced into the clip boundary parameters of a Reader, and is anyway irregularly shaped rather than a rectangle.
So, instead of using Reader parameters, an existing boundary is used to clip data either with a FeatureReader transformer or with a Clipper transformer.
Selecting the Existing Area
If the existing area feature is a single feature in a dataset, then it can be read into the workspace and used immediately.
If, however, it is part of a larger dataset, then it needs to be filtered from the rest of the data. If the Reader has a where clause (and the feature can be identified in that way) then it is the most efficient way of filtering the data:

Here the data from a Geodatabase is filtered down to the one required feature using a WHERE clause. If the Reader has no WHERE clause parameter, then the full dataset can be read and the required feature filtered out using transformers such as the Tester or TestFilter.
FeatureReader
The existing area feature is routed into the FeatureReader like so:
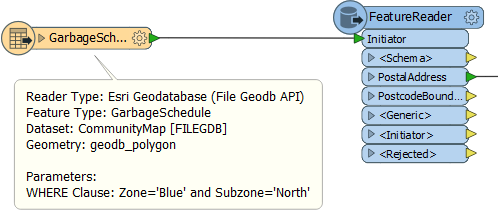
Here a single garbage schedule area (Blue zone, north) is passed to the FeatureReader for use as a filter. The idea is to return only addresses that fall inside that garbage zone. The parameters dialog is set up like this:
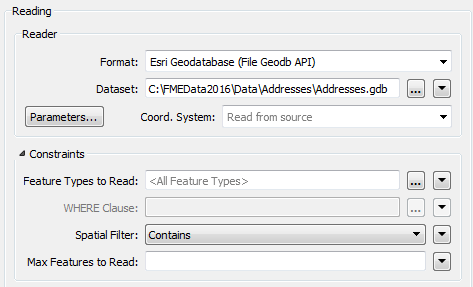
Notice that the FeatureReader is set to read from an address geodatabase. The Spatial Filter parameter tells the transformer to only read features inside the incoming area feature.
Clipper
The Clipper transformer is a means to spatially filter data that is already read into a workspace (other similar transformers are the PointOnAreaOverlayer, or the SpatialFilter).
Here the address database is read into a workspace and the Clipper used to filter out those addresses that fall inside the chosen garbage collection zone:

| Ms Vector says... |
|
In the above examples, the results of the Clipper and FeatureReader will be exactly the same. So why is the FeatureReader the preferred option? Pick all the reasons that apply:
1. It can be quicker and more resource efficient 2. It allows multiple areas to be used as the existing areas 3. It work with raster data 4. It has more choices for spatial filtering |