Introduction to FME Workbench
Let's take a closer look at FME Workbench, firstly how to start it. To start Workbench - besides double-clicking an fmw file - locate Workbench in the Windows start menu:
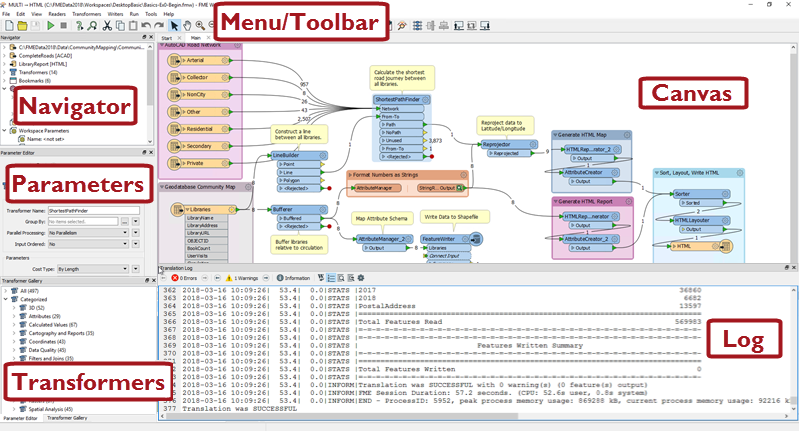
Major Components of FME Workbench
The FME Workbench user interface has a number of major components:
Canvas
As we've seen, the FME Workbench canvas is where to define a translation. It is the primary window within Workbench:
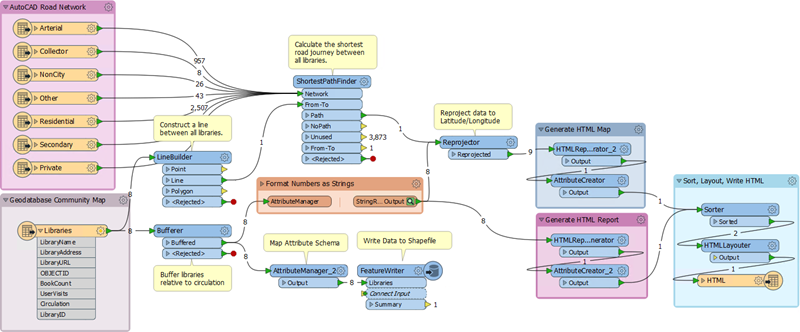
By default the workspace reads from left to right; data source on the left, transformation tools in the center, and data destination on the right. Connections between each item represent the flow of data and may branch in different directions, merge together, or both.
Menu/Toolbar
The menubar and toolbar contain a number of tools: for example, tools for navigating around the Workbench canvas, controlling administrative tasks, and adding or removing readers/writers:

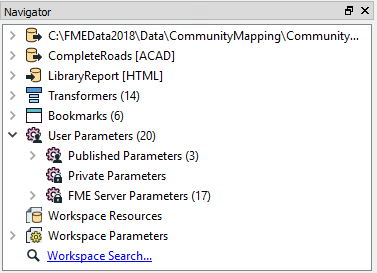
Navigator
The Navigator window is a structured list of parameters that represent and control all of the components of a translation:
Transformer Gallery
The transformer gallery is a tool for the location and selection of FME transformation tools.

The number of transformers (above, 497) will vary depending on the version of FME and any optional custom transformers installed.
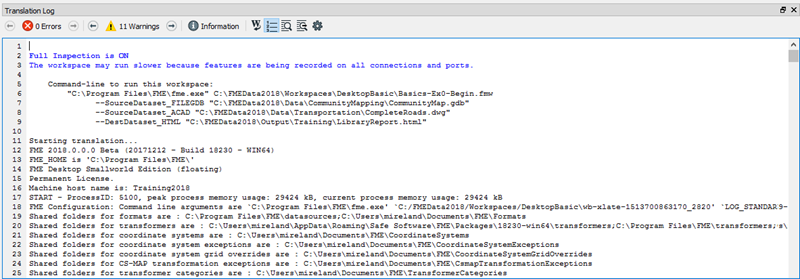
Translation Log
The translation log reports on translations and other actions. Information includes any warning or error messages, translation status, length of translation, and the number of features processed:
Parameter Editor Window
The Parameter Editor window is for editing parameters for objects on the canvas window:

As the next section will show, you can open or close these windows at will, or rearrange them into any configuration that you like.
| Miss Vector says... |
|
As we work through the course the questions will get harder. Still, these are pretty easy:
Which of the following applications is NOT a part of FME Desktop? 1. FME Workbench 2. FME Integration Console 3. FME Server Console 4. FME Data Inspector FME Workbench allows you to define flows of data in which way... 1. Graphically 2. Telepathically 3. Problematically 4. By writing lots of code in C++ or Java |