Bounding Box
A bounding box - also known as a search envelope - is simply a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME a bounding box can be defined in several ways, but the easiest is to use a set of parameters.
All FME readers have parameters to define the bounding box (envelope) of data that is being read:
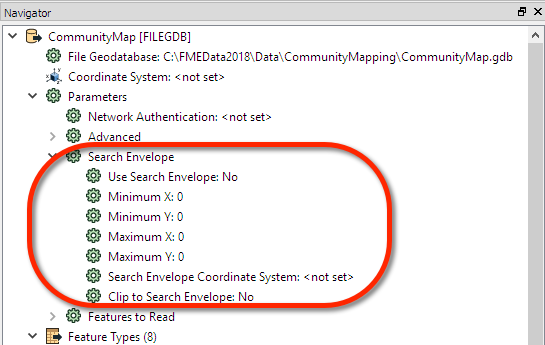
The parameters include not just the coordinates of the bounding box, but also a parameter to define the coordinate system. The coordinate system for the bounding box does not have to be the same as the coordinate system the data is stored in, meaning tools that return lat/long coordinates can be used to clip data stored in UTM (very useful for mobile FME Server solutions).
There is also a parameter specifying whether to clip features to the exact envelope boundary. If set to No then features that overlap the boundary will be included in their full (unclipped) form. For a Data Download service, it's more likely that this parameter should be set to Yes.
The workspace author can manually set these parameters, but by publishing them, the end-user is able to enter values that define the extent of the data he/she is interested in.
| Ms. Analyst says… |
| Using reader parameters is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because it can mean FME does not have to read the entire dataset first and then clip it to size; it can read only what data is necessary. It applies to both vector and raster datasets and is particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index. |
Web Mapping and Bounding Boxes
Bounding box parameters are particularly useful when a web mapping application (for example Google Earth) is requesting data. The application will provide the extents of the current map view and the workspace restricts itself to reading features within those extents.
This, of course, is done using published parameters. The parameters in the workspace need to be given specific names when published, as follows:
- bboxWest
- bboxEast
- bboxNorth
- bboxSouth
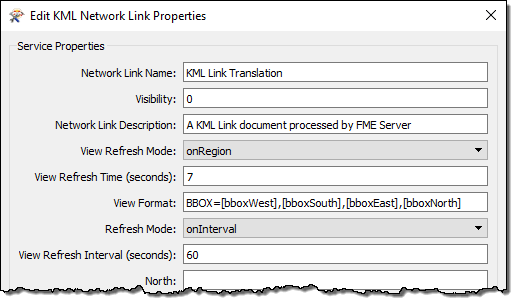
A KML Network Link service will automatically make use of these parameters. In fact, if you click the Edit button for KML Network Link properties (in the Publish to FME Server wizard), you will notice how these are used to pass information back to the workspace: