1.4 Token Management
There are many ways to get a token to use for authentication.
Ways to get a token
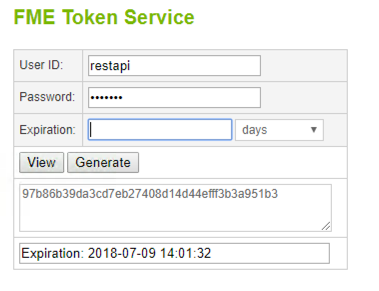
1) Through the FME token page
To generate a token visit:
http://<yourServerHost>/fmetoken/
or http://localhost/fmetoken/ if you are using a training computer.
Once you access your server, you will be asked to verify your username and your password and be asked to specify when you would like your token to expire. The maximum amount of time you can issue a token for is two years.
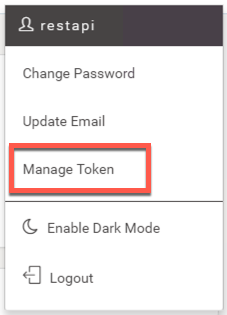
2) Through your FME Server
http://<yourServerHost>/fmeserver/#/home
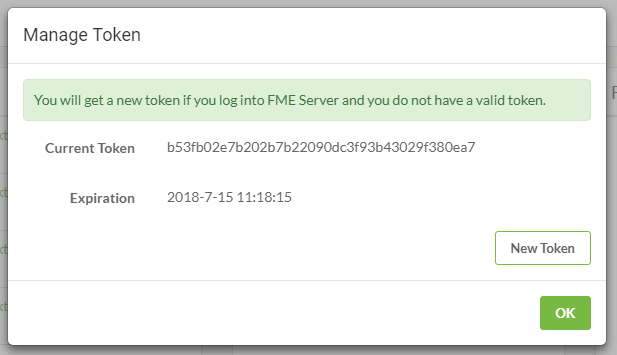
On the FME Server, click on the user icon. Then click Manage Token.
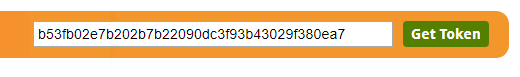
3) Through the REST API Homepage
http://<yourServerHost>/fmerest/apidoc/v3/
On the top right-hand corner of the page you will see a Green Button that says "Get Token". Click here, to get a token or look up your existing token.
Tokens and Users
You may also request and manage tokens through the web application. Often users will hard code the Guest user into the application. This prevents the user from having to log in to access the data. The methods of this will be discussed in a later tutorial on building a web application.
Using a Token in a Call
There are two methods of including a token to the FME Server. You may include the token in the query parameter and the authorization header. The actual methods of using these different practices will be discussed later in the tutorial. However, for now, it's important to know the pros and cons of each method.
Query Parameter- You may include the token right in the Request URL of the call. This is a quick and easy way to use a call that requires a token.
http://<yourServerHost>/fmerest/v3/info?fmetoken=<yourToken>
However, this is not recommended because the token will be visible in the URL.
Authorization Header- You may also include the token in the Request Header. This is the preferred method because the token will be more hidden inside the call.
Troubleshooting Authorization Errors
If a call is not authorized you will receive an error code back from the system. You may receive a Forbidden or Unauthorized message. Forbidden (code 403) means the request was understood but refused. This indicates you do not have the correct permissions to complete the request. Unauthorized (code 401) indicates the credentials were missing or incorrect. This may occur if the request needs a token and it is not present, or the token is expired.