Reader Dataset Parameter
Of course, perhaps the most important parameter is that which defines the dataset to be read. This too is found in the Navigator window:
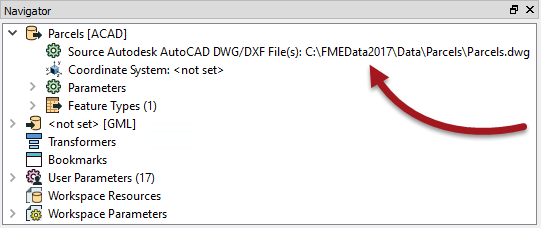
As usual, double-clicking the parameter opens a dialog for it to be changed. You can change the dataset being read by selecting any other dataset - of the same format - within that dialog.
Dataset Selection: Multiple Files
As long as the format is file-based (i.e. not a database) a reader is capable of reading multiple source datasets:
To do this, when selecting the dataset to read simply select multiple files from the source folder, instead of a single file.
Dataset Selection: Multiple Folders
In a similar way, multiple files can be selected from multiple folders, but this requires a slightly different dialog:

This tool opens an advanced file browser to allow you to select source files that reside in different folders; for example:
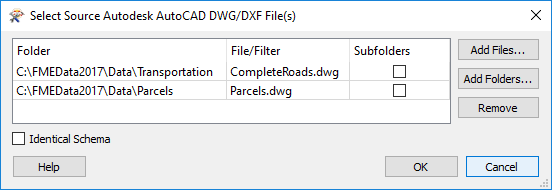
You can even select a single folder and have the reader read all files of the correct type from it. This is advantageous because the workspace can continue to function correctly even if the source files change (for example, some are deleted and others are added).
Dataset Selection: Web Sources
Besides local filesystems, it's also possible to select source data from web-based filesystems such as Dropbox or Google Drive:
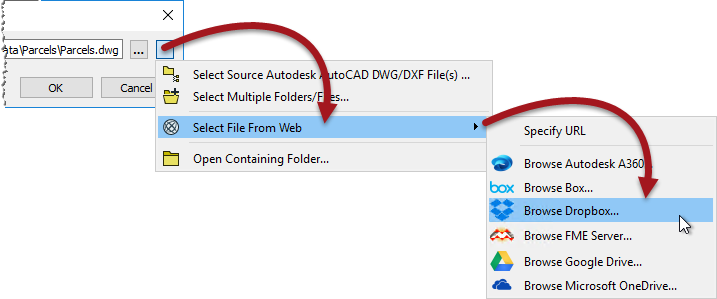
To take advantage of this requires a pre-defined web connection to the chosen filesystem. If you haven't previously defined such a connection then you will be prompted to add one when choosing this method of selecting source data.
You can also define a connection at any time using Tools > FME Options > Web Connections on the FME Workbench menubar
| NEW |
| Although the ability to enter a URL for a source dataset has existed in FME for some time, the ability to browse web-based filesystems such as Dropbox and Google Drive is new for FME2017 |
File Dataset Types
When dealing with files it's useful to consider datasets as existing in two differnt forms: File-based and Folder-based
File-Based Datasets
A file-based dataset is just that: a single file that contains all layers of data. A format of this type has an internal structure that assigns data to different layers within the file.
Good examples of this are:
- AutoCAD DWG: Each DWG file is a dataset containing its own set of layers
- Microsoft Excel: Each Excel file is a dataset containing a set of sheets
In this scenario the dataset parameter is simply a pointer to the location of the file(s), here a single AutoCAD dataset:
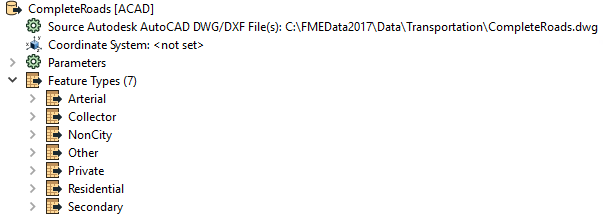
Notice that the dataset is comprised of a number of feature types (layers): Arterial, Collector, NonCity, etc.
Folder-Based Datasets
A folder-based dataset is still made up of files (of course). However, a format of this type DOES NOT have an internal way to define layers. Therefore each layer becomes a separate file within a folder.
Good examples of this are:
- Esri Shapefile: To store different layers requires multiple Shapefiles: e.g. roads.shp and railways.shp
- Comma-Separated (CSV): To store separate tables requires two separate CSV files
In this scenario the dataset parameter is a pointer to the individual files, here a set of layers in a shapefile dataset:

Again notice there are a number of feature types; but there is a separate file for each of these.
| Sister Intuitive says... |
|
Both File or Folder dataset parameters can be pointers to a Zip file. You simply select the zip file in the source parameter and FME will extract the data when it is being read.
Similarly, a File or Folder dataset can be read directly from a URL. Simply enter the URL into the source parameter. For Folder datasets the URL must point to a zip file containing all of the relevant files. |