Conditional Filtering
Transformers that filter don’t transform data content, yet surveys show that they’re the most commonly used type of transformer there is!
What is Filtering?
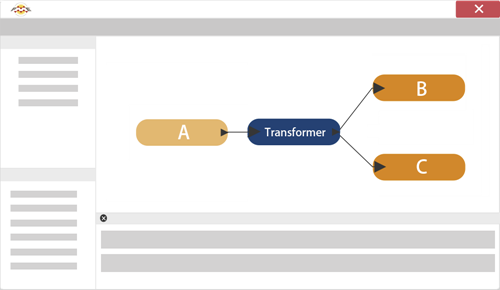
Filtering is the technique of subdividing data as it flows through a workspace. It’s the case where there are multiple output connections from a transformer, each of which carries data to be processed in a different way. Here (for example) incoming stream A is filtered into two new streams, B and C:
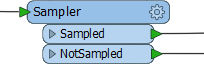
A filtering transformer may be any transformer with multiple output ports, such as the GeometryFilter or Sampler transformers, the latter of which create a sample selection of data and separates it out through Sampled and NotSampled output ports.
However, these are mostly in-built, fixed tests. Conditional filtering is where the decision about which features are output to which connection is decided by some form of user-defined test or condition. The Tester transformer is the most obvious example of this. It carries out a test and has different output ports for features that pass and fail the test.
Transformers that Filter
Many transformers in the Filter and Joins category carry out these tests and redirect data according to the results.
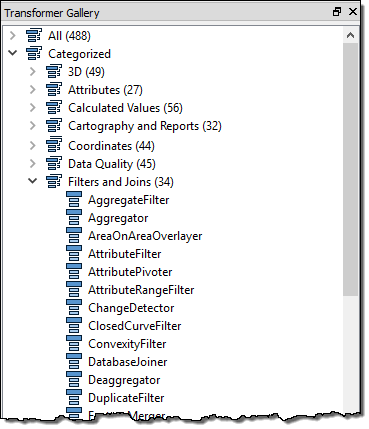
Although the Tester transformer is the most used of this category, there are many other transformers such as the TestFilter,GeometryFilter, AttributeFilter, SpatialFilter, and Sampler.
| Miss Vector says... |
|
Time for a quick question. How many filtering transformers in the Filter and Joins category appear in the top-25 Most-Valuable Transformers list?
1. Two (2) 2. Four (4) 3. Six (6) 4. Eight (8) |