| Exercise 3 | Reader Feature Types |
| Data | City Parks (MapInfo TAB) Walking Trail (CSV) Food Vendors/Water Fountains (File Geodatabase) |
| Overall Goal | Create a set of data for mapping a recreational event |
| Demonstrates | Handling and Controlling Reader Feature Types |
| Start Workspace | C:\FMEData2017\Workspaces\DesktopBasic\Components-Ex3-Begin.fmw |
| End Workspace | C:\FMEData2017\Workspaces\DesktopBasic\Components-Ex3-Complete.fmw |
Let's continue your work on the fundraising walk project.
In case you forgot, the city is hosting a fundraising walk for a major charity and you have been tasked with using FME to put together the data that will form the event map.
In this part of the project we’ll add another of the source datasets to the workspace.
1) Start Workbench
Start Workbench (if necessary) and open the workspace from Exercise 2. Alternatively you can open C:\FMEData2017\Workspaces\DesktopBasic\Components-Ex3-Begin.fmw
2) Add Reader
The existing workspace already has various Readers; now it needs one for loading a layer of food vendor data. This is stored in the Community Mapping Geodatabase
Select Readers > Add Reader from the menubar in Workbench. When prompted fill in the following details:
| Reader Format | Esri Geodatabase (File Geodb API) |
| Reader Dataset | C:\FMEData2017\Data\CommunityMapping\CommunityMap.gdb |
| .1 UPDATE |
| In FME2017.1 the format is now called Esri Geodatabase (File Geodb Open API) |
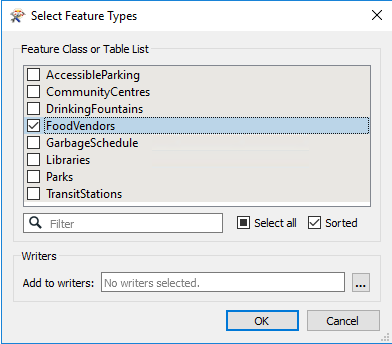
This dataset contains several tables, but we only need one of them. So, when prompted, deselect all feature types and leave only FoodVendors selected:
3) Import DrinkingFountains Feature Type
No sooner have you added the FoodVendors layer to the workspace than the telephone rings. It is the event organizers. As well as showing food vendors on the map, they now want to also show the location of drinking fountains.
Muttering under your breath, Click Readers > Import Feature Types on the menubar.
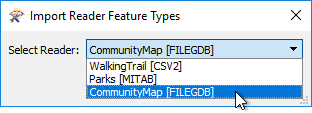
The first dialog that pops up will ask you which reader you want to import the feature type to. Select the Community Mapping Geodatabase:
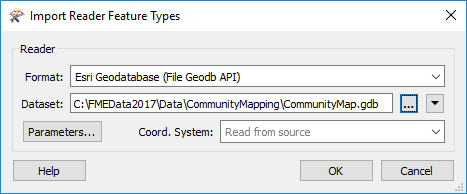
Now you are prompted which dataset you wish to import the feature type from. Enter the details (as above) for the Community Mapping Geodatabase (but don't click OK yet):
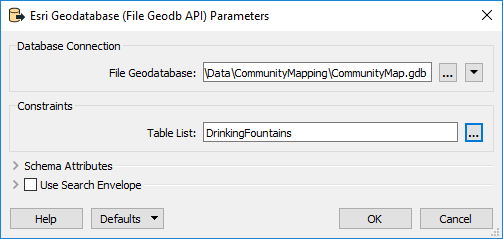
Before clicking OK, click the Parameters button. In the parameters dialog select the DrinkingFountains table to read:
Click OK and OK again. This will add the DrinkingFountains feature type to the workspace.
4) Remove FoodVendors Feature Type
Again the phone rings. This time the organizers say they have changed their mind again and no longer need the FoodVendors table at all.
Well, this is a very simple fix. Put down the phone, click on the FoodVendors feature type, and press the delete key. The feature type is now removed from the workspace.
5) Connect to Reprojector
Like the parks data, we don't really need to reproject the Geodatabase data - it is already in UTM83-10 - but it makes for a tidier workspace, so connect the DrinkingFountains feature type to the Reprojector transformer.
6) Add Clipper
If you recall the Community Maps dataset covers the entire city, and yet we're restricting the map to the park boundaries. To cut the excess data away we'll use a Clipper transformer, so add one to the canvas. Then...
- Connect the Tester:Passed port to the Clipper:Clipper port.
- Connect the Reprojector:Reprojected port to the Clipper:Clippee port:
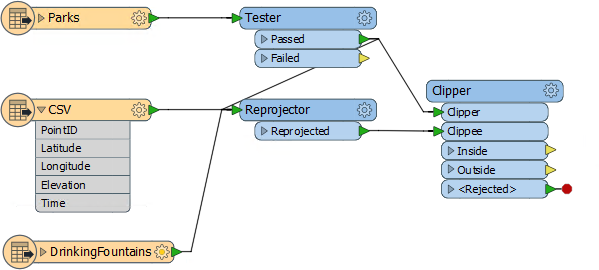
You can check the transformer parameters, but the defaults should be fine for this project. Again, all data is being routed through the Clipper, even if it doesn't need to be so, in order to make a tidier workspace.
7) Run Workspace
Again, add Inspectors and run the workspace to ensure the result is what we are expecting.
Map tiles by Stamen Design, under CC-BY-3.0. Data by OpenStreetMap, under CC-BY-SA.
| CONGRATULATIONS |
By completing this exercise you have learned how to:
|