Alternative Dynamic Schema Sources
In general, the schema for a dynamic translation comes from either the source dataset itself or from a different dataset (such as the database table the data is being written to).
However, there are two other scenarios for providing the output schema:
- A schema can come from a lookup table (text file or spreadsheet) in which definitions are stored
- A schema can be defined dynamically as a list of attributes in a workspace
Table-Based Schemas
In this scenario, the output schema is stored as some form of a table in a text file or spreadsheet; for example:
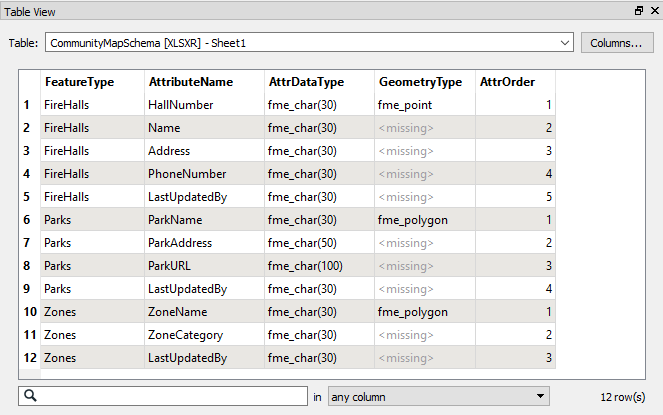
Here the author has listed a series of feature types, attributes, and geometry types that define the output schema. In FME they would use this schema by adding a Resource Reader. The format of the Resource Reader would be Schema (From Table):

In the parameters dialog for this reader there are parameters to specify which fields in the table represent which parts of the schema:
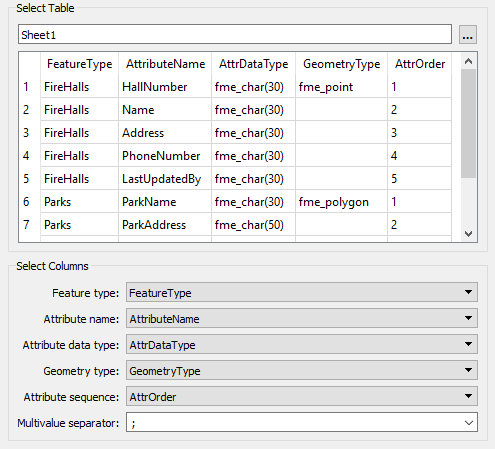
Geometry type is optional but used in this example.
Attribute sequence is another optional parameter. It defines a field in the table that records the order that attributes should appear in.
Then, of course, this reader must be used as the source for the output schema:
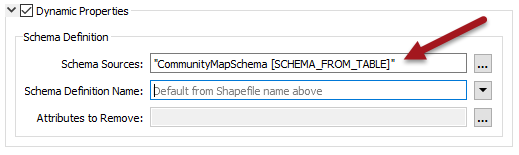
As always, the incoming attributes must be mapped to the outgoing schema. The best way here is the SchemaMapper transformer since it too can use a lookup table to create its mappings.
| Sister Intuitive says… |
| A significant advantage of this method is that you don’t need to edit the workspace, or edit a dataset, to make schema changes. Once you change the output schema in the table, then that is automatically applied in the FME translation. That’s heavenly! |
Constructed Attribute Schemas
This scenario is a way to construct an attribute schema using lists in FME. The schema is defined by using attributes in the list, for example:
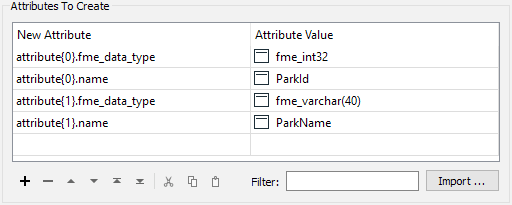
The writer is told to use this schema in preference to any others by selecting it as the Source Schema:

FME Data Types
Both of the two preceding tools allow the user to define attribute type in an output schema. There are a set of valid datatypes in FME, which are as follows:
| General Field Type | Specific Field Types |
|---|---|
| Character Fields | fme_varchar(width), fme_char(width), fme_char |
| Integer Fields | fme_uint8, fme_int16, fme_uint16, fme_int32, fme_uint32, fme_int64,fme_uint64 |
| Numeric Fields | fme_decimal(width,decimal), fme_real32, fme_real64 |
| Date-Time Fields | fme_datetime, fme_time, fme_date |
| Other Fields | fme_buffer, fme_boolean |
| Miss Vector says… |
|
The ability to construct a dynamic schema from attributes in a workspace has lots of possibilities. In fact, one of these FME transformers automatically creates dynamic schema attributes specifically so you can create a new schema. Which is it?
1. SchemaMapper 2. AttributePivoter 3. PythonCaller 4. Clipper |